This guide provides a step-by-step approach to setting up a robust blockchain development environment, covering essential software, programming languages, frameworks, and tools.
Points
- Importance of version control in blockchain development.
- Steps for installing essential programming languages.
- Overview of blockchain development frameworks and tools.
- Setting up local blockchain networks and smart contract development.
Setting up a comprehensive blockchain development environment is crucial for efficient and effective blockchain application development. This guide covers everything from version control systems to installing essential software and configuring local blockchain networks.
1. Version Control Systems
Using a version control system like Git is essential for managing your codebase, collaborating with others, and tracking changes. Platforms like GitHub or GitLab facilitate efficient code management, team collaboration, and version tracking.
2. Installing Essential Software
Programming Languages
Blockchain development often involves multiple programming languages. Here are the installation steps for some common languages:
JavaScript/TypeScript:
Python:
Go:
Rust:
Docker
Docker is a vital tool for creating consistent development environments. Here are the steps to install Docker:
3. Blockchain Development Frameworks and Tools
General Setup
Setting up a development environment involves various tools and libraries that support blockchain irrespective of the specific blockchain. Tools like Truffle and Hardhat provide comprehensive development environments.
Popular Frameworks
- Hyperledger Fabric: Designed for large enterprises, Hyperledger Fabric offers a modular architecture for private blockchains.
- Tendermint: Known for its high performance, Tendermint supports Byzantine Fault T
Tolerant (BFT) consensus algorithms, ensuring robust and efficient blockchain operations.
Containerization and Virtualization
Docker helps maintain consistent environments across different machines. By using Docker containers, you can package all dependencies and configurations, making it easy to set up and tear down development environments.
4. Setting Up Local Blockchain Networks
General Tools
Several tools are useful for managing and running local blockchain networks:
Docker Compose: This tool is used for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. Here are the installation steps for Docker Compose:
Kubernetes: Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Here are the installation steps for Kubernetes:
Running Local Nodes
Setting up local nodes is crucial for testing your blockchain applications in a controlled environment. Here are the steps for setting up a local node:
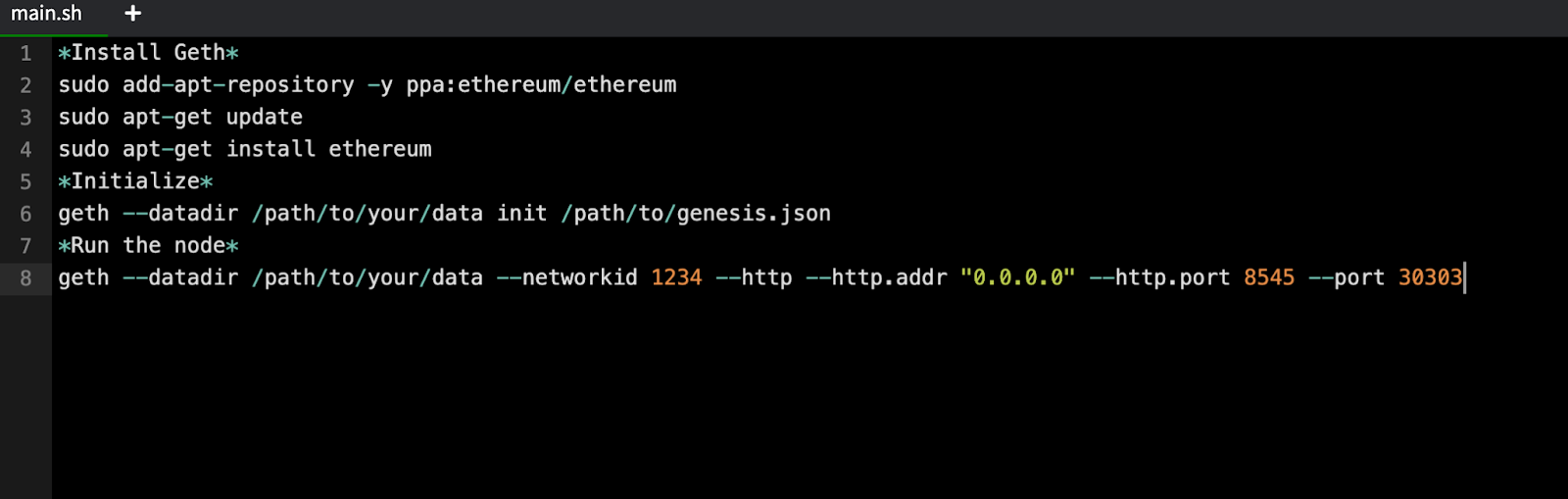
Using Virtual Machines
Virtual machines (VMs) allow you to experiment with your applications without affecting your local environment, providing an additional layer of abstraction and isolation.
5. Smart Contract Development
Common Languages
Smart contracts are typically written in Solidity and Rust:
Solidity:
npm install -g solc
solc --version
Rust:
rustup target add wasm32-unknown-unknown
Compilers and Linters
Compilers and linters are essential for writing high-quality smart contracts. Compilers translate the code into executable bytecode, while linters ensure code quality and adherence to standards.
Compiling a Contract
Solidity:
solc --bin --abi --optimize -o build/ YourContract.sol
Create a .solhint.json file for linting:
{
"extends": "solhint:recommended",
"rules": {
"indent": ["error", 4],
"quotes": ["error", "double"]
}
}
Rust:
Install Clippy:
rustup component add clippy
Create a Clippy.toml file:
[clippy]
warnings_as_errors = true
Writing Smart Contracts
When writing smart contracts, follow these best practices:
- Ensure modularity and reusability.
- Conduct thorough security audits.
- Optimize for gas efficiency.
- Perform extensive testing.
- Document your code well.
- Use SafeMath libraries.
- Check return values and handle errors.
- Avoid hardcoding values.
- Maintain a consistent coding style.
- Implement access control mechanisms.
- Regularly update dependencies.
- Use events for logging.
- Utilize standard libraries.
- Implement multisignature wallets.
- Plan for long-term maintenance.
6. Testing and Debugging
Testing Frameworks
Testing is vital for robust development. Mocha and Chai are essential for testing contracts in JavaScript. Mocha is a test framework, and Chai is an assertion library.
Debugging Tools
Debugging involves finding and fixing bugs. Tools like Remix and GDB are useful for debugging blockchain applications.
Continuous Testing
Continuous testing ensures your code is constantly validated. Tools for Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) help automate the testing process whenever changes are made.
7. Deployment Tools
General Deployment Strategies
There are several deployment strategies:
- Local Deployment: Using tools like Ganache and Docker for local, controlled deployment.
- Testnet Deployment: Testing the application in a real-world environment without real assets.
- Mainnet Deployment: Deploying to the main network where real transactions occur, requiring thorough testing.
- Automated Deployment: Using CI/CD pipelines for automated and repeatable deployment processes.
Scripting and Automation
You can write scripts for automation using tools like Hardhat:
8. Using Cloud Services
Cloud services provide scalability and reliability for deploying blockchain nodes and smart contracts. Common services include:
AWS: Amazon Web Services offers EC2 instances for running nodes and AWS Lambda for serverless execution.
Azure: Azure Blockchain Service helps manage blockchain networks, with Azure Functions and Azure DevOps for implementation.
GCP: Google Cloud’s Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and Compute Engine support blockchain nodes, with Cloud Functions and Cloud Build for setup.
9. Connecting to External Networks
Configuration
Configuring connections involves setting up network configurations. For example, in Ethereum:
{
"networks": {
"mainnet": {
"accounts": ["0xYOUR_PRIVATE_KEY"]
}
}
}
API and Libraries
APIs and libraries simplify interactions with external networks. Popular ones include:
Ethers.js:
const { ethers } = require("ethers");
const provider = new ethers.providers.InfuraProvider("homestead", "YOUR-PROJECT-ID");
Polka.js:
const { ApiPromise, WsProvider } = require('@polkadot/api');
const provider = new WsProvider('wss://rpc.polkadot.io');
const api = await ApiPromise.create({ provider });
Web3.js:
const Web3 = require('web3');
Wallet Integration
Wallet integration allows user interactions with the blockchain through transactions. Examples include:
Metamask:
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
WalletConnect:
const WalletConnectProvider = require("@walletconnect/web3-provider");
const provider = new WalletConnectProvider({ infuraId: "YOUR-INFURA-ID" });
10. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
General CI/CD Tools
GitHub Actions: GitHub Actions lets you set up CI/CD pipelines:
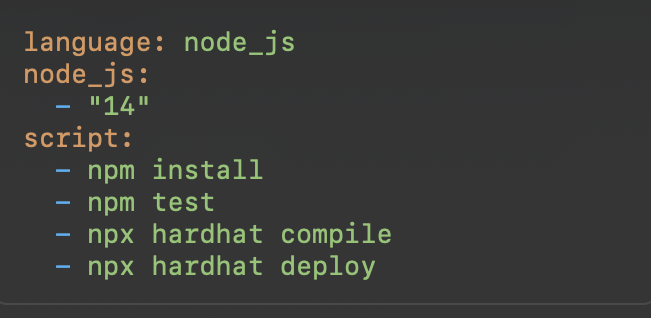
Travis CI:
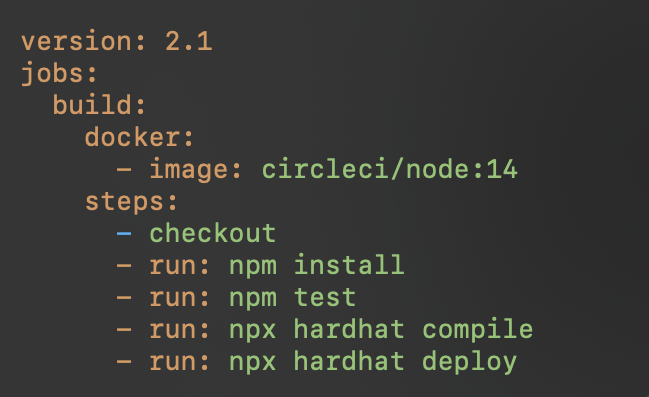
CircleCI: CircleCI provides robust CI/CD options for blockchain projects:
Automated Testing and Deployment
Writing workflows for automated testing and deployment ensures consistent code quality and quick iterations.
11. Security Tools
General Security Practices
Security is paramount in blockchain development:
- Conduct regular code reviews.
- Implement precise access controls.
- Perform regular audits.
Static Analysis Tools
Static analysis tools identify vulnerabilities in your code:
Mythril: A security analysis tool for Ethereum smart contracts.
Slither: A static analysis tool for Solidity contracts.
Regular Audits
Conduct regular internal and external audits to identify and fix issues before contracts are exploited.
12. Best Practices
Folder Structure
Maintain a clean and organized folder structure for easy access and a clutter-free environment.
Environment Variables
Use .env files and libraries like dotenv for managing environment variables securely.
Documentation
Documentation is crucial for understanding and maintaining code:
- Maintain a comprehensive README file.
- Add comments in the code.
- Use project wikis or documentation APIs
Documentation (continued)
Use project wikis or documentation APIs to ensure detailed and accessible project information.
13. Conclusion
Setting up the right development environment is crucial for building efficient, robust, and secure blockchain applications. Following the steps and strategies mentioned in this guide will help you create a well-structured and productive setup. Continuously learning and adapting to new tools and technologies will further enhance your development process, keeping you at the forefront of blockchain innovation. Happy Coding!
